Your Favorite Aunt Can Read a Newspaper Only if It Is Within 11.0 Cm of Her Eyes.
Mastering Physics Solutions Affiliate 27 Optical Instruments
Mastering Physics Solutions
Affiliate 27 Optical Instruments Q.1CQ
Why is it restful to your optics to gaze off into the distance?
Solution:
When a person with normal vision relaxes the cilliary muscles of the eye. An object at infinity is in focus. In a nearsighted person , however , a totally relaxed eye focuses just out to a finite distance from the eye- the far point. Thus a person with condition is said to be nearsighted because objects well-nigh the eye can be focused , where equally objects beyond the far signal are fuzzy.
Chapter 27 Optical Instruments Q.1P
· CEPredict/Explain BIO Octopus Eyes To focus its optics, an octopus does not change the shape of its lens, every bit is the instance in humans. Instead, an octopus moves its rigid lens back and forth, every bit in a camera. This changes the distance from the lens to the retina and brings an object into focus. (a) If an object moves closer to an octopus, must the octopus move its lens closer to or farther from its retina to keep the object in focus? (b) Choose the best explanation from amongst the following:
I. The lens must move closer to the retina—that is, farther away from the object—to recoup for the object moving closer to the middle.
II. When the object moves closer to the eye, the image produced by the lens will exist further behind the lens; therefore, the lens must move further from the retina.
Solution:
(a) To focus its optics, an octopus does not alter the shape of its lens, as in the case in humans. Instead, an octopus moves its rigid lens back and forth, as in a photographic camera. This changes the distance from the lens to the retina and brings an object into focus.
If an object moves closer to an octopus, the paradigm produced by the lens will be further behind the lens. Therefore, in order to keep the object in focus, the octopus must move its lens farther from its retina.
(b) The right caption is option (II).
Option (Two): When the object moves closer to the eye, the image produced past the lens volition exist farther backside the lens; therefore, the lens must movement further from the retina.
Affiliate 27 Optical Instruments Q.2CQ
If a lens is cut in half through a plane perpendicular to its surface, does information technology bear witness only half an prototype?
Solution:
No, when the lens is cutting into one-half through aeroplane perpendicular to its surface the focal length lens remains the aforementioned. So, the lens now shows the same prototype.
Chapter 27 Optical Instruments Q.2P
Your friend is 1.9 thousand tall. (a) When she stands 3.2 chiliad from yous, what is the height of her epitome formed on the retina of your eye? (Consider the heart to consist of a thin lens 2.five cm from the retina.) (b) What is the height of her prototype when she is 4.2 m from you?
Solution:


Chapter 27 Optical Instruments Q.3CQ
If your near-point distance is N, how close can you stand to a mirror and all the same be able to focus on your paradigm?
Solution:

Affiliate 27 Optical Instruments Q.3P
Which forms the larger image on the retina of your eye: a 43-ft tree seen from a distance of 210 ft, or a 12-in. flower viewed from a distance of 2.0 ft?
Solution:


Chapter 27 Optical Instruments Q.4CQ
When yous open your optics underwater, everything looks blurry. Tin this be thought of as an extreme case of nearsightedness or farsightedness? Explain.
Solution:
It looks blurry under water because there will be less refraction of low-cal. When it passes from water to your cornea than when it passes from air to your cornea. Therefore, your eyes but aren't converging light enough when they are in water. Since if your eyes exercise not converge light as much as they tin can then we can say farsighted ness is acquired.

Chapter 27 Optical Instruments Q.4P
Approximating the eye as a single thin lens 2.60 cm from the retina, find the middle'southward almost-point distance if the smallest focal length the centre tin can produce is ii.20 cm.
Solution:

Chapter 27 Optical Instruments Q.5CQ
Would you benefit more from a magnifying drinking glass if your nearpoint distance is 25 cm or if it is 15 cm? Explicate.
Solution:
A person with the larger nigh-point altitude benefits more from the magnifier. Since a person with the smaller nearly-betoken distance can examine an object at closer range than a person with the larger near-bespeak altitude.
Affiliate 27 Optical Instruments Q.5P
Referring to Problem 4, what is the focal length of the eye when information technology is focused on an object at a distance of (a) 285 cm and (b) 28.5 cm?
Solution:


Affiliate 27 Optical Instruments Q.6CQ
When you use a unproblematic magnifying drinking glass, does it matter whether y'all hold the object to be examined closer to the lens than its focal length or farther away? Explicate.
Solution:

Aye, it matters; a unproblematic magnifier is nothing more than a convex lens.
From the above figures nosotros can say that a convex lens forms the images enlarged only when the object is closer to the lens than its focal lengths.
Affiliate 27 Optical Instruments Q.6P

Solution:



Chapter 27 Optical Instruments Q.7CQ
Is the final image produced by a telescope real or virtual? Explain.
Solution:
The image formed past the objective is essentially at the focal signal of the heart-slice. This ways the eyepiece forms a virtual paradigm at infinity that the observer can view with a relaxed eye.


Chapter 27 Optical Instruments Q.7P
BIO The focal length of the human eye is approximately i.vii cm. (a) What is the f-number for the human being middle in vivid light, when the pupil diameter is 2.0 mm? (b) What is the f-number in dim light, when the pupil bore has expanded to 7.0 mm?
Solution:

Chapter 27 Optical Instruments Q.8CQ
Does chromatic aberration occur in mirrors? Explicate.
Solution:
No, because the paradigm formed by a mirror is due to the reflection of light, but non the refraction of light. Chromatic aberration occurs in lenses considering of refraction of unlike colors of light. Since the reflection of low-cal does not depends on color, the lite of all colors aptitude in the same fashion by a mirror; therefore there will exist no chromatic aberration in the case of mirror.
Chapter 27 Optical Instruments Q.8P
IP A camera with a 55-mm-focal-length lens has discontinuity settings of 2.viii, 4, viii, xi, and sixteen. (a) Which setting has the largest aperture bore? (b) Calculate the 5 possible aperture diameters for this camera.
Solution:



Chapter 27 Optical Instruments Q.9P
The actual frame size of "35-mm" moving picture is 24 mm × 36 mm. You want to take a photograph of your friend, who is 1.9 m tall. Your camera has a 55-mm-focal-length lens. How far from the photographic camera should your friend stand up in order to produce a 36-mm- tall image on the picture?
Solution:


Chapter 27 Optical Instruments Q.10P
To completely fill a frame of "35-mm" film, the image produced by a camera must exist 36 mm high. If a photographic camera has a focal length of 150 mm, how far away must a 2.0-m-tall person stand to produce an prototype that fills the frame?
Solution:


Affiliate 27 Optical Instruments Q.11P
· · You are taking a photo of a poster on the wall of your dorm room, so yous can't back away whatsoever farther than 3.0 m to have the shot. Tire poster is 0.80 m wide and 1.2 m tall, and you want the image to fit in the 24-mm × 36-mm frame of the film in your camera. What is the longest focal length lens that volition piece of work?
Solution:

Chapter 27 Optical Instruments Q.12P
A photograph is properly exposed when the discontinuity is set to f/viii and the shutter speed is 125. Find the approximate shutter speed needed to give the same exposure if the aperture is changed to f/ii.4.
Solution:


Chapter 27 Optical Instruments Q.13P
You are taking pictures of the beach at sunset. But before the Sun sets, a shutter speed of f/11 produces a properly exposed movie. Before long afterwards the Sun sets, however, your light meter indicates that the scene is but one-quarter equally brilliant as before. (a) If you lot don't change the aperture, what estimate shutter speed is needed for your second shot? (b) If, instead, y'all keep the shutter speed at one/100 s, what estimate f-terminate will exist needed for the second shot?
Solution:


Chapter 27 Optical Instruments Q.14P
· · IP You lot are taking a photograph of a horse race. A shutter speed of 125 at f/five.6 produces a properly exposed prototype, merely the running horses give a blurred image. Your camera has f-stops of 2, 2.8, 4, 5.6, viii, 11, and 16. (a) To use the shortest possible exposure fourth dimension (i.eastward., highest shutter speed), which f-end should you apply? (b) What is the shortest exposure time you can utilize and however get a properly exposed image?
Solution:


Chapter 27 Optical Instruments Q.15P
The Hale Telescope The 200-in. (5.08-one thousand) diameter mirror of the Hale telescope on Mount Palomar has a focal length ƒ = 16.9 yard. (a) When the detector is placed at the focal point of the mirror (the "prime focus"), what is the f-ratio for this telescope? (b) The coudé focus arrangement uses additional mirrors to curve the light path and increase the effective focal length to 155.4 one thousand. What is the f-ratio of the telescope when the coudé focus is beingness used? (Coudé is French for "elbow," since the light path is "bent similar an elbow." This arrangement is useful when the light needs to be focused onto a distant musical instrument.)
Solution:

Chapter 27 Optical Instruments Q.16P
· CEPredict/Explain Ii professors arc stranded on a deserted island. Both wear glasses, though i is nearsighted and the other is farsighted. (a) Which person's glasses should be used to focus the rays of the Sun and start a burn down? (b) Choose the best explanation from among the following:
I. A nearsighted person can focus close, so that person'southward glasses should be used to focus the sunlight on a piece of moss at a distance of a couple inches.
2. A farsighted person tin't focus shut, so the glasses to correct that person'due south vision are converging. A converging lens is what yous need to concentrate the rays of the Sun.
Solution:
1403-27-16P SA Code: 6078.
SR Code:5784
(a). Nosotros know that the farsighted person uses converging glasses. The convex lens focuses light from an object inside near betoken to produce an image that is beyond the nearly betoken. Therefore the farsighted person'due south glasses are used to offset the fire.
(b)Therefore the best explanation is 2
Chapter 27 Optical Instruments Q.17P
· CE A clerk at the local grocery store wears glasses that brand her eyes look larger than they actually are. Is the clerk nearsighted or farsighted? Explain.
Solution:

Chapter 27 Optical Instruments Q.18P
CE The umpire at a baseball game game wears glasses that brand his eyes expect smaller than they actually are. Is the umpire nearsighted or farsighted? Explain.
Solution:
Past wearing diverging lens the eyes appear smaller than the actual ane. If the Umpire wears diverging lens then he should be nearsighted.
Affiliate 27 Optical Instruments Q.19P
Construct a ray diagram for Active Example 27–2.
Solution:


Affiliate 27 Optical Instruments Q.20P
The cornea of a normal human centre has an optical power of +43.0 diopters. What is its focal length?
Solution:

Affiliate 27 Optical Instruments Q.21P
A myopic student is shaving without his spectacles. If Iris eyes have a far signal of 1.6 m, what is the greatest distance he can stand from the mirror and still see his image conspicuously?
Solution:


Chapter 27 Optical Instruments Q.22P
An eyeglass prescription calls for a lens with an optical power of +two.vii diopters. What is the focal length of this lens?
Solution:

Chapter 27 Optical Instruments Q.23P
Ii thin lenses, with f1 = +25.0 cm and f2 = —42.5 cm, are placed hr contact. What is the focal length of this combination?
Solution:

Chapter 27 Optical Instruments Q.24P
Two sparse lenses have refractive powers of +4.00 diopters and —two.35 diopters. What is the refractive power of the two if they are placed in contact? (Note that these are the aforementioned two lenses described in the previous trouble.)
Solution:



Chapter 27 Optical Instruments Q.25P
Two concave lenses, each with ƒ = —12 cm, are separated by 6.0 cm. An object is placed 24 cm in forepart of 1 of the lenses. Find (a) the location and (b) the magnification of the last image produced past this lens combination.
Solution:




Chapter 27 Optical Instruments Q.26P
IP BIO The focal length of a relaxed human centre is approximately 1.7 cm. When we focus our eyes on a shut-upward object, nosotros tin modify the refractive power of the center by about sixteen diopters. (a) Does the refractive ability of our eyes increase or subtract by 16 diopters when we focus closely? Explain. (b) Calculate the focal length of the center when nosotros focus closely.
Solution:

Chapter 27 Optical Instruments Q.27P
IP BIO Diopter Change in Diving Cormorants Double- crested cormorants (Phalacrocorax auritus) are extraordinary birds—they tin can focus on objects in the air, but like we can, simply they tin besides focus underwater as they pursue their prey. To do so, they have ane of the largest adaptation ranges in nature— that is, they tin can change the focal length of their eyes past amounts that are greater than is possible in other animals. When a cormorant plunges into the ocean to catch a fish, it tin modify the refractive power of its eyes by near 45 diopters, as compared to merely 16 diopters of change possible in the homo eye. (a) Should this change of 45 diopters be an increase or a decrease? Explicate. (b) If the focal length of the cormorant's eyes is 4.2 mm before it enters the water, what is the focal length later the refractive power changes by 45 diopters?
Solution:

Chapter 27 Optical Instruments Q.28P
A converging lens of focal length 8.000 cm is 20.0 cm to the left of a diverging lens of focal length –6.00 cm. A money is placed 12.0 cm to the left of the converging lens. Find (a) the location and (b) the magnification of the coin'due south final image.
Solution:



Chapter 27 Optical Instruments Q.29P
Repeat Problem 28, this time with the coin placed 18.0 cm to the right of the diverging lens.
Solution:



Chapter 27 Optical Instruments Q.30P
Find the focal length of contact lenses that would allow a farsighted person with a near-point distance of 176 cm to read a book at a distance of 10.one cm.
Solution:

Affiliate 27 Optical Instruments Q.31P
Find the focal length of contact lenses that would allow a nearsighted person with a 135-cm far point to focus on the stars at night.
Solution:

Affiliate 27 Optical Instruments Q.32P
What focal length should a pair of contact lenses accept if they are to correct the vision of a person with a almost indicate of 56 cm?
Solution:

Affiliate 27 Optical Instruments Q.33P
A nearsighted person wears contacts with a focal length of –8.5 cm. Tf this person's far-point altitude with her contacts is 8.five yard, what is her uncorrected far-point distance?
Solution:

Chapter 27 Optical Instruments Q.34P
Without Iris glasses, Isaac can see objects conspicuously only if they are less than 4.5 grand from his eyes. What focal length glasses worn ii.ane cm from his eyes volition let Isaac to see distant objects clearly?
Solution:

Chapter 27 Optical Instruments Q.35P
A person whose nigh-bespeak distance is 49 cm wears a pair of glasses that are 2.0 cm from her eyes. With the aid of these glasses, she can now focus on objects 25 cm away from her optics. Find the focal length and refractive ability of her glasses.
Solution:


Chapter 27 Optical Instruments Q.36P
A pair of eyeglasses is designed to allow a person with a far- point distance of two.50 m to read a road sign at a distance of 25.0 thousand. Detect the focal length required of these glasses if they are to exist worn (a) ii.00 cm or (b) ane.00 cm from the eyes.
Solution:


Chapter 27 Optical Instruments Q.37P
IP Your favorite aunt can read a newspaper only if it is within fifteen.0 cm of her eyes. (a) Is your aunt nearsighted or farsighted? Explain. (b) Should your aunt clothing spectacles that are converging or diverging to better her vision? Explicate. (c) How many diopters of refractive power must her spectacles have if they are worn ii.00 cm from the eyes and allow her to read a newspaper at a altitude of 25.0 cm?
Solution:


Chapter 27 Optical Instruments Q.38P
IP The relaxed eyes of a patient accept a refractive power of
48.5 diopters. (a) Is this patient nearsighted or farsighted? Explain. (b) If this patient is nearsighted, find the far signal. If this person is farsighted, discover the nearly point. (For the purposes of this problem, treat the eye as a single-lens organization, with the retina 2.40 cm from the lens.)
Solution:


Affiliate 27 Optical Instruments Q.39P
IP Y'all are comfortably reading a book at a distance of 24 cm. (a) What is the refractive power of your eyes? (b) Does the refractive ability of your optics increase or decrease when you move the volume farther away? Explain. (For the purposes of this problem, care for the eye equally a single-lens arrangement, with the retina 2.40 cm from the lens.)
Solution:

Chapter 27 Optical Instruments Q.40P
Without glasses, your Uncle Albert can sec things conspicuously just if they are between 25 cm and 170 cm from his eyes. (a) What ability eyeglass lens will correct your uncle's myopia? Assume the lenses will sit 2.0 cm from his eyes. (b) What is your uncle's nearly point when wearing these glasses?
Solution:


Affiliate 27 Optical Instruments Q.41P
A 2.05-cm-alpine object is placed 30.0 cm to the left of a converging lens with a focal length f1 = 20.5 cm. A diverging lens, with a focal length f2 = –42.five cm, is placed 30.0 cm to the correct of the start lens. How tall is the final epitome of the object?
Solution:



Chapter 27 Optical Instruments Q.42P
A simple camera telephoto lens consists of ii lenses. The objective lens has a focal length f1 = +39.0 cm. Precisely 36.0 cm behind this lens is a concave lens with a focal length f2 = –10.0 cm. The object to be photographed is 4.00 m in front of the objective lens. (a) How far behind the concave lens should the flick be placed? (b) What is the linear magnification of this lens combination?
Solution:



Chapter 27 Optical Instruments Q.43P
IP With unaided vision, a librarian tin can focus just on objects that lie at distances betwixt 5.0 m and 0.fifty thou. (a) Which type of lens (converging or diverging) is needed to correct his nearsightedness? Explain. (b) Which type of lens volition correct his farsightedness? Explain. (c) Detect the refractive power needed for each part of the bifocal eyeglass lenses that volition give the librarian normal visual vigil from 25 cm out to infinity. (Assume the lenses rest 2.0 cm from his optics.)
Solution:


Chapter 27 Optical Instruments Q.44P
IP With unaided vision, a physician tin can focus only on objects that lie at distances between 5.0 m and 0.50 m. (a) Which type of lens (converging or diverging) is needed to correct her nearsightedness? Explain. (b) Which type of lens will correct her farsightedness? Explain. (c) Discover the refractive power needed for each part of the bifocal contact lenses that volition give the md normal visual vigil from 25 cm out to infinity.
Solution:
The md can focus but on objects that lie at distances between five.0 thou and 0.50 thou.then doctor has nearsightedness.
(a)
In a nearsighted a person, however, a totally relaxed eyes focuses but out to a finite distance from the middle. Thus a person with this status is said to be nearsighted considering objects near the heart can be focused.
The diverging lens can produce an prototype of a afar object at physician far point distance, so, the dr. should wear glasses with diverging lenses.
(b)
A Converging lens in front of the centre can correct for farsightedness. The convex lens focuses light from an object inside the near point to produce an image that is beyond the nigh point. The eye tin at present focus on the image of the object.

Chapter 27 Optical Instruments Q.45P
A person's prescription for her new bifocal glasses calls for a refractive ability of –0.445 diopter in the distance-vision part, and a ability of +i.85 diopters in the close-vision part. What are the near and far points of this person's uncorrected vision? Assume the spectacles are ii.00 cm from the person'due south eyes, and that the person's near-betoken distance is 25.0 cm when wearing the glasses.
Solution:



Affiliate 27 Optical Instruments Q.46P
A person's prescription for his new bifocal eyeglasses calls for a refractive power of –0.0625 diopter in the distance-vision function and a power of +ane.05 diopters in the close-vision part. Bold the spectacles rest 2.00 cm from Iris optics and that the corrected near-bespeak distance is 25.0 cm, determine the about and far points of this person's uncorrected vision.
Solution:





Chapter 27 Optical Instruments Q.47P
Ii lenses, with f1 = +20.0 cnr and f2 = +xxx.0 cm, are placed on the x centrality, as shown in Figure 27-22. An object is fixed 50.0 cm to the left of lens ane, and lens ii is a variable distance 10 to the right of lens 1. Find the lateral magnification and location of the final image relative to lens ii for the following cases: (a) x = 115 cm; (b) 10 = thirty.0 cm; (c) ten = 0. (d) Show that your result for part (c) agrees with the relation for the effective focal length of two lenses in contact, ane/feff = l/f1 + i/f2.

Solution:






Chapter 27 Optical Instruments Q.48P
A converging lens with a focal length of four.0 cm is to the left of a second identical lens. When a plume is placed 12 cm to the left of the first lens, the final image is the same size and orientation every bit the feather itself. What is the separation between the lenses?
Solution:


Chapter 27 Optical Instruments Q.49P
The Moon is 3476 km in diameter and orbits the Earth at an average altitude of 384,400 km. (a) What is the angular size of the Moon as seen from Earth? (b) A penny is nineteen mm in diame- ter. How far from your eye should the penny be held to produce the aforementioned angular diameter every bit the Moon?
Solution:

Chapter 27 Optical Instruments Q.50P
A magnifying glass is a unmarried convex lens with a focal length of ƒ = +14.0 cm. (a) What is the angular magnification when this lens forms a (virtual) image at —∞? How far from the object should the lens be held? (b) What is the angular magnification when this lens forms a (virtual) image at the person'due south near betoken (causeless to be 25 cm)? How far from the object should the lens be held in this example?
Solution:


Chapter 27 Optical Instruments Q.51P
IP A pupil has two lenses, ane of focal length f1 = five.0 cm and the other with focal length f2 = 13 cm. (a) When used as a simple magnifier, which of these lenses can produce the greater magnification? Explain, (b) Find the maximum magnification produced by each of these lenses.
Solution:

Chapter 27 Optical Instruments Q.52P
A beetle 4.73 mm long is examined with a simple magnifier of focal length f = 10.1 cm. If the observer's eye is relaxed while using the magnifier, and has a near-point distance of 25.0 cm, what is the apparent length of the protrude?
Solution:

Chapter 27 Optical Instruments Q.53P
To engrave wishes of good luck on a watch, an engraver uses a magnifier whose focal length is 8.65 cm. If the paradigm formed past the magnifier is at the engraver'southward nearly betoken of 25.6 cm, find (a) the altitude between the watch and the magnifier and (b) the angular magnification of the engraving. Assume the magnifying glass is direct in front of the engraver's optics.
Solution:

Affiliate 27 Optical Instruments Q.54P
A jeweler examines a diamond with a magnifying glass. If the most-point distance of the jeweler is 20.8 cm, and the focal length of the magnifying glass is 7.50 cm, find the athwart magnification when the diamond is held at the focal point of the magnifier. Assume the magnifying glass is directly in front end of the jeweler's eyes.
Solution:

Chapter 27 Optical Instruments Q.55P
in Problem 54, notice the athwart magnification when the diamond is held 5.59 cm from the magnifying glass.
Solution:

Chapter 27 Optical Instruments Q.56P
A person with a near-betoken distance of 25 cm finds that a magnifying drinking glass gives an angular magnification that is 1.5 times larger when the image of the magnifier is at the near point than when the image is at infinity. What is the focal length of the magnifying glass?
Solution:

Chapter 27 Optical Instruments Q.57P
CE You have ii lenses: lens i with a focal length of 0.45 cm and lens two with a focal length of 1.ix cm. If you construct a microscope with these lenses, which one should you use equally the objective? Explicate.
Solution:

Chapter 27 Optical Instruments Q.58P
A chemical compound microscope has an objective lens with a focal length of 2.two cm and an eyepiece with a focal length of v.four cm. If the prototype produced by the objective is 12 cm from the objective, what magnification does this microscope produce?
Solution:

Affiliate 27 Optical Instruments Q.59P
BIO A typical cherry-red claret cell subtends an angle of only ane.ix × x–five rad when viewed at a person's virtually-point distance of 25 cm. Suppose a reddish blood prison cell is examined with a compound microscope in which the objective and eyepiece are separated by a distance of 12.0 cm. Given that the focal length of the eyepiece is two.7 cm, and the focal length of the objective is 0.49 cm, observe the magnitude of the angle subtended by the cherry blood prison cell when viewed through this microscope.
Solution:


Chapter 27 Optical Instruments Q.60P
The medium-power objective lens in a laboratory microscope has a focal length fobjective = iv.00 mm. (a) If this lens produces a lateral magnification of –40.0, what is its "working distance"; that is, what is the distance from the object to the objective lens? (b) What is the focal length of an eyepiece lens that will provide an overall magnification of 125?
Solution:


Chapter 27 Optical Instruments Q.61P
A compound microscope has the objective and eyepiece mounted in a tube that is eighteen.0 cm long. The focal length of the eyepiece is 2.62 cm, and the near-point distance of the person using the microscope is 25.0 cm. If the person tin view the image produced by the microscope with a completely relaxed centre, and the magnification is –4525, what is the focal length of the objective?
Solution:

Chapter 27 Optical Instruments Q.62P
In Problem 61, what is the distance between the objective lens and the object to be examined?
Solution:


Affiliate 27 Optical Instruments Q.63P
The butt of a compound microscope is xv cm in length. The specimen will be mounted i.0 cm from the objective, and the eyepiece has a 5.0-cm focal length. Determine the focal length of the objective lens.
Solution:

Chapter 27 Optical Instruments Q.64P
A compound microscope uses a 75.0-mm lens equally the objective and a 2.0-cm lens equally the eyepiece. The specimen will be mounted 122 mm from the objective. Determine (a) the butt length and (b) the full magnification produced past the microscope.
Solution:


Chapter 27 Optical Instruments Q.65P
The "tube length" of a microscope is defined to be the departure between the (objective) image distance and objective focal length: L = di – fobjective. Many microscopes are standardized to a tube length of 50 = 160 mm. Consider such a microscope whose objective lens has a focal length fobjective = 7.50 mm. (a) How far from the object should this lens exist placed? (b) What focal length eyepiece would give an overall magnification of –55? (c) What focal length eyepiece would requite an overall magnification of –110?
Solution:


Chapter 27 Optical Instruments Q.66P
CE Two telescopes of dissimilar length produce the same angular magnification. Is the focal length of the long telescope's eyepiece greater than or less than the focal length of the brusque telescope's eyepiece? Explain.
Solution:
The angular magnification is the ratio between focal length of the objective to the focal length of the eye piece. Now the angular magnification for both the telescopes is same, and also given that the length of one telescope is greater than the other, by considering the above two conditions we can say that the focal lengths of eye piece and objective are greater in longer telescope
Affiliate 27 Optical Instruments Q.67P
CE To construct a telescope, you are given a lens with a focal length of 32 mm and a lens with a focal length of 1600 mm. (a) On the basis of focal length alone, which lens should be the objective and which the eyepiece? Explicate. (b) What magnification would this telescope produce?
Solution:

Chapter 27 Optical Instruments Q.68P
A grade schoolhouse student plans to build a 35-power telescope every bit a science fair project. She starts with a magnifying drinking glass with a focal length of v.0 cm as the eyepiece. What focal length is needed for her objective lens?
Solution:

Affiliate 27 Optical Instruments Q.69P
A 55-power refracting telescope has an eyepiece with a focal length of v.0 cm. How long is the telescope?
Solution:

Chapter 27 Optical Instruments Q.70P
An amateur astronomer wants to build a small refracting telescope. The only lenses available to him have focal lengths of 5.00 cm, x.0 cm, twenty.0 cm, and thirty.0 cm. (a) What is the greatest magnification that can be obtained using 2 of these lenses? (b) How long is the telescope with the greatest magnification?
Solution:

Affiliate 27 Optical Instruments Q.71P
A pirate sights a distant ship with a spyglass that gives an angular magnification of 22. If the focal length of the eyepiece is xi mm, what is the focal length of the objective?
Solution:

Chapter 27 Optical Instruments Q.72P
A telescope has lenses with focal lengths f1 = +30.0 cm and f2 = +5.0 cm. (a) What distance between the two lenses will permit the telescope to focus on an infinitely afar object and produce an infinitely distant paradigm? (b) What distance betwixt the lenses will permit the telescope to focus on an object that is v.0 thousand away and to produce an infinitely distant image?
Solution:


Chapter 27 Optical Instruments Q.73P
Jason has a 25-ability telescope whose objective lens has a focal length of 120 cm. To brand his sister announced smaller than normal, he turns the telescope around and looks through the objective lens. What is the angular magnification of his sister when viewed through the "wrong" end of the telescope?
Solution:

Affiliate 27 Optical Instruments Q.74P
Roughing Information technology with Science A professor shipwrecked on Hooligan's Island decides to build a telescope from his eyeglasses and some kokosnoot shells. Fortunately, the professor'south eyes crave dissimilar prescriptions, with the left lens having a power of +5.0 diopters and the right lens having a power of +2.0 diopters. (a) Which lens should he utilize as the objective? (b) What is the athwart magnification of the professor's telescope?
Solution:

Affiliate 27 Optical Instruments Q.75P
Galileo'south Telescope Galileo'southward first telescope used a convex objective lens with a focal length ƒ = 1.7 m and a concave eyepiece, as shown in Figure 27-23. When this telescope is focused on an infinitely distant object, and produces an infinitely distant prototype, its athwart magnification is +3.0. (a) What is the focal length of the eyepiece? (b) How far apart are the 2 lenses?

Solution:

Chapter 27 Optical Instruments Q.76P
The Moon has an angular size of 0.50° when viewed with unaided vision from Earth. Suppose the Moon is viewed through a telescope with an objective whose focal length is 53 cm and an eyepiece whose focal length is 25 mm. What is the angular size of the Moon as seen through this telescope?
Solution:

Affiliate 27 Optical Instruments Q.77P
In Problem 76, an eyepiece is selected to give the Moon an angular size of 15°. What is the focal length of this eyepiece?
Solution:

Chapter 27 Optical Instruments Q.78P
A telescope is 275 mm long and has an objective lens with a focal length of 257 mm. (a) What is the focal length of the eyepiece? (b) What is the magnification of this telescope?
Solution:

Affiliate 27 Optical Instruments Q.79GP
CE Predict/Explicate BIO Intracorneal Band An intracomeal band is a pocket-size plastic device implanted in a person'due south cornea to modify its curvature. By changing the shape of the cornea, the intracorneal ring can correct a person's vision. (a) If a person is nearsighted, should the ring increase or subtract the cornea's curvature? (b) Choose the best explanation from among the following:
I. The intracorneal ring should increase the curvature of the cornea so that it bends light more. This will let it to focus on light coming from far away.
Two. The intracorneal band should decrease the curvature of the cornea so information technology's flatter and bends calorie-free less. This will allow parallel rays from far abroad to exist focused.
Solution:
1403-27-79GP SA: 6078
SR: 5784
RID: 267
Picture the problem:
An intra-corneal band is a small plastic device implanted in a person's cornea to change its curvature, and so nosotros can correct a person's vision.
Strategy:
A nearsighted person'south eye converges the calorie-free coming into short altitude, that is, the focal length of the eye is less than the distance from lens to the retina. When a person sees that an object at infinity forms an image in front of the retina, because of the elongation of the eye.
To correct this condition, we need to undo some of the excess convergence produced by the eye, so that the concluding epitome falls on the retina.
Solution:
(a) If a person is near sighted, placing the intra-corneal ring should decrease the cornea's curvature, then that focal length of the middle is equal to the altitude from lens to the retina. Because to focus on far objects, the focal length (or radius of curvature) should exist larger hence the curvature of the lens that is cornea should exist smaller.
(b) Therefore the best explanation is 2.
The intra-corneal ring should subtract the curvature of the cornea so it flattens and bends calorie-free less. This allows parallel rays from far abroad to exist focused.
Chapter 27 Optical Instruments Q.80GP
· CE BIO The lens in a normal human center, with aqueous sense of humor on one side and vitreous humour on the other side, has a refractive power of xv diopters. Suppose a lens is removed from an eye and surrounded by air. In this case, is its refractive ability greater than, less than, or equal to 15 diopters? Explain.
Solution:
We know that the refractive alphabetize of air is less than the refractive index of any medium. If we consider the lens is placed in air, the light rays volition bend more in air than in aqueous or vitreous medium.
This is because the departure in index of refraction between air and lens is greater than the difference between index of refraction of any medium other than air and the lens.
The light rays refract more when the lens is placed in air. Therefore the refractive power of the lens in air is greater than xv diopters.
Chapter 27 Optical Instruments Q.81GP
CE An optical organisation consists of two lenses, one with a focal length of 0.l cm and the other with a focal length of 2.3 cm. If the separation betwixt the lenses is 12 cm, is the instrument a microscope or a telescope? Explain.
Solution:

Chapter 27 Optical Instruments Q.82GP
CE Air optical organization consists of two lenses, one with a focal length of 50 cm and the other with a focal length of 2.5 cm. If the separation between the lenses is 52.v cm, is the instrument a microscope or a telescope? Explicate.
Solution:

Chapter 27 Optical Instruments Q.83GP
CE Predict/Explain BIO Treating Cataracts When the lens in a person's heart becomes clouded by a cataract, the lens can exist removed with a procedure called phacoemulsification and replaced with a man-made intraocular lens. The intraocular lens restores clear vision, but its focal length cannot be changed to let the user to focus at different distances. In most cases, the intraocular lens is adapted for viewing of distant objects, and cosmetic glasses are worn when viewing nearby objects. (a) Should the refractive power of the corrective spectacles exist positive or negative? (b) Choose the best explanation from among the following:
I. The refractive power should be positive—converging— because the intraocular lens will make the person farsighted.
Two. A negative refractive power is required to bring the focal bespeak of the intraocular lens in from infinity to a finite value.
Solution:
1403-27-83GP SA Code: 6078.
SR Code: 5784
(a)
Refractive power of corrective glasses should exist positive. Considering to view nearby objects, converging lenses (power is positive) are needed as the intraocular lens tin can non change its focal length to allow the user to focus at closer distances.
(b)
Therefore the all-time caption is I
Affiliate 27 Optical Instruments Q.84GP
IP Tire greatest refractive ability a patient's eyes tin produce is 44.1 diopters. (a) Is this patient nearsighted or farsighted? Explain. (b) If this patient is nearsighted, find the far indicate. If this person is farsighted, find the almost point. (For the purposes of this problem, treat the eye as a unmarried-lens organization, with the retina 2.40 cm from the lens.)
Solution:



Affiliate 27 Optical Instruments Q.85GP
IP You are observing a rare species of bird in a distant tree with your unaided eyes. (a) What is the refractive power of your eyes? (b) Does the refractive power of your eyes increment or decrease when you shift your view to the guidebook in your hands? Explain. (For the purposes of this problem, treat the eye equally a single-lens arrangement, with the retina 2.40 cm from the lens.)
Solution:

Chapter 27 Optical Instruments Q.86GP
Galileo's original telescope (Figure 27–23) used a convex objective and a concave eyepiece. Use a ray diagram to prove that this telescope produces an upright prototype when a distant object is being viewed. Assume that the eyepiece is to the right of the object and that the right-hand focal signal of the eyepiece is just to the left of the objective's correct-hand focal point. hour addition, assume that the focal length of the eyepiece has a magnitude that is about one-quarter the focal length of the objective.
Solution:


Chapter 27 Optical Instruments Q.87GP
IP For each of the following cases, utilise a ray diagram to show that the angular sizes of tire image and the object are identical if both angles are measured from the heart of the lens. (a) A convex lens with the object outside the focal length. (b) A convex lens with the object inside the focal length. (c) A concave lens with the object outside the focal length. (d) Given that the athwart size does not modify, how does a uncomplicated magnifier work? Explain.
Solution:

Chapter 27 Optical Instruments Q.88GP
IP You have two lenses, with focal lengths f1 = +2.60 cm and f2 = +20.4 cm. (a) How would you lot arrange these lenses to form a magnified paradigm of the Moon? (b) What is the maximum angular magnification these lenses could produce? (c) How would you lot suit the same 2 lenses to course a magnified image of an insect? (d) If you lot utilise the magnifier of part (c) to view an insect, what is the angular magnification when the insect is held 2.ninety cm from the objective lens?
Solution:


Affiliate 27 Optical Instruments Q.89GP
BIO Tire eye is really a multiple-lens organisation, but we can estimate it with a single-lens system for most of our purposes. When the heart is focused on a distant object, the optical power of the equivalent single lens is +41.4 diopters. (a) What is the constructive focal length of the center? (b) How far in front of the retina is this "equivalent lens" located?
Solution:

Affiliate 27 Optical Instruments Q.90GP
BIO Fitting Contact Lenses with a Keratometer When a patient is being fitted with contact lenses, the curvatrue of the patient'south cornea is measured with an instrument known as a keratometer. A lighted object is held near the eye, and the keratometer measures the magnification of the image formed past reflection from the front of the conrea. If an object is held x.0 cm in front end of a patient's middle, and the reflected prototype is magnified by a cistron of 0.035, what is the radius of curvature of the patient's cornea?
Solution:

Chapter 27 Optical Instruments Q.91GP
Pricey Stamp A rare 1918 "Jenny" postage stamp, depicting a misprinted, upside-down Curtiss JN-4 "Jenny" aeroplane, sold at auction for $525,000. A collector uses a unproblematic magnifying glass to examine the "Jenny," obtaining a linear magnification of 2.5 when the stamp is held two.76 cm from the lens. What is the focal length of the magnifying drinking glass?
Solution:

Affiliate 27 Optical Instruments Q.92GP
IP A person needs glasses with a refractive power of –1.35 diopters to be able to focus on distant objects. (a) Is this person nearsighted or farsighted? Explicate. (b) What is this person's (unaided) far bespeak?
Solution:


Chapter 27 Optical Instruments Q.93GP
IP BIO A Large Eye The largest centre ever to exist on Earth belonged to an extinct species of ichthyosaur, Temnodontosaurus platyodon. This creature had an heart that was 26.4 cm in diameter. Information technology is estimated that this ichthyosaur likewise had a relatively large educatee, giving it an constructive discontinuity setting of about f/1.1. (a) Assuming its pupil was i-third the diameter of the eye, what was the approximate focal length of the ichthyosaur'due south centre? (b) When the ichthyosaur narrowed its pupil in vivid lite, did its f-number increase or decrease? Explain.
Solution:

Chapter 27 Optical Instruments Q.94GP
Consider a Galilean telescope, equally illustrated in Effigy 27–23, synthetic from 2 lenses with focal lengths of 75.6 cm and –18.0 mm. (a) What is the distance between these lenses if an infinitely distant object is to produce an infinitely distant image? (b) What is the angular magnification when the lenses are separated by the distance calculated in part (a)?
Solution:

Chapter 27 Optical Instruments Q.95GP
A converging lens forms a virtual object 12 cm to the right of a 2nd lens that has a refracting power of three.75 diopter. (a) Where is the image? (b) Is the paradigm real or virtual? Explain.
Solution:

Affiliate 27 Optical Instruments Q.96GP
A farsighted person uses glasses with a refractive power of iii.6 diopters. The glasses are worn 2.5 cm from his eyes. What is this person's near point when not wearing glasses?
Solution:


Chapter 27 Optical Instruments Q.97GP
Landing on an Shipping Carrier The Long-Range Lineup Organisation (LRLS) used to ensure prophylactic landings on aircraft carriers consists of a series of Fresnel lenses of different colors. Each lens focuses low-cal in a different, specific direction, and hence which light a airplane pilot sees on arroyo determines whether the plane is in a higher place, below, or on the proper landing path. The basic idea behind a Fresnel lens, which has the aforementioned optical properties as an ordinary lens, is shown in Figure 27-24, along with a photo of the LRLS. Suppose an object (a lightbulb in this case) is 17.1 cm behind a Fresnel lens, and that the corresponding image is a altitude di = d in front of the lens. If the object is moved to a distance of 12.0 cm behind the lens, the image distance doubles to di =2d. hi the LRLS, information technology is desired to have the image of the lightbulb at infinity. What object distance will requite this result for this particular lens?

Solution:

Chapter 27 Optical Instruments Q.98GP
When using a telescope to photograph a faint astronomical object, you lot need to maximize the amount of lite energy that falls on each square millimeterof the image on the motion picture. For a given telescope and object, the full light that falls on the film is proportional to the length of the exposure, so a long exposure will reveal fainter objects than a short exposure. Bear witness that for a given length of exposure, the brightness of the image is inversely proportional to the square of the f-number of the telescope organization.
Solution:

Chapter 27 Optical Instruments Q.99GP
A Cassegrain astronomical telescope uses two mirrors to form the image. Tire larger (concave) objective mirror has a focal length f1 = +fifty.0 cm. A small convex secondary mirror is mounted 43.0 cm in front of the primary. As shown in Figure 27-25, light is reflected from the secondary through a hole in the centre of the primary, thereby forming a real image 8.00 cm behind the chief mirror. What is the radius of curvature of the secondary mirror?

Solution:


Chapter 27 Optical Instruments Q.100GP
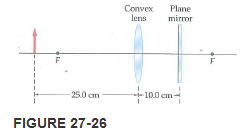
IP A convex lens (f = 20.0 cm) is placed 10.0 cm in forepart of a aeroplane mirror. A matchstick is placed 25.0 cm in front of the lens, as shown in Figure 27-26. (a) If you look through the lens toward the mirror, where will you lot see the prototype of the matchstick? (b) Is the image real or virtual? Explicate. (c) What is the magnification of the image? (d) Is the image upright or inverted?

Solution:



Chapter 27 Optical Instruments Q.101GP
Repeat Problem 100 for the case where the converging lens is replaced with a diverging lens with ƒ = –twenty.0 cm. Everything else in the trouble remains the same.
Solution:


Chapter 27 Optical Instruments Q.102GP
· · · Repeat Trouble 47 for the case where lens one is replaced with a diverging lens with f1 = –20.0 cm. Everything else in the problem remains the aforementioned.
Solution:




Affiliate 27 Optical Instruments Q.103GP
· · · The bore of a collimated laser axle can be expanded or reduced past using two converging lenses, with focal lengths f1 and f2, mounted a distance f1 + f2 from each other, as shown in Figure 27-27. What is the ratio of the two beam diameters, (d1/d2), expressed in terms of the focal lengths?

Solution:


Affiliate 27 Optical Instruments Q.104GP
Consider three lenses with focal lengths of 25.0 cm, –xv.0 cm, and 11.0 cm positioned on the x centrality at 10 = 0,x = 0.400 m, and ten = 0.500 one thousand, respectively. An object is at x = –122 cm. Find (a) the location and (b) the orientation and magnification of the final image produced by this lens organization.
Solution:




Chapter 27 Optical Instruments Q.105GP
· · · Because a concave lens cannot form a real image of a existent object, it is hard to measure its focal length precisely. Ane method uses a 2nd, convex, lens to produce a virtual object for the concave lens. Nether the proper weather condition, the concave lens will form a real image of the virtual object! A student conducting a laboratory project on concave lenses makes the post-obit observations: When a lamp is placed 42.0 cm to the left of a particular convex lens, a real (inverted) image is formed 37.5 cm to the right of the lens. The lamp and convex lens are kept in place while a concave lens is mounted 15.0 cm to the right of the convex lens. A existent image of the lamp is now formed 35.0 cm to the right of the concave lens. What is the focal length of each lens?
Solution:

Chapter 27 Optical Instruments Q.106GP
· · · A person with a nigh-point distance N uses a magnifying glass with a focal length f. Bear witness that the greatest magnification that can be achieved with this magnifier is M = i + North/f.
Solution:



Chapter 27 Optical Instruments Q.107PP
A patient receives a rigid IOL whose focus cannot be changed—it is designed to provide clear vision of objects at infinity. The patient volition use corrective contacts to permit for close vision. Should the refractive power of the corrective contacts be positive or negative?
Solution:


Chapter 27 Optical Instruments Q.108PP
Referring to the previous problem, notice the refractive powerof contacts that will let the patient to focus on a book at adistance of 23.0 cm.
A. 0.0435 diopter
B. 0.230 diopter
C. 4.35 diopters
D. 8.seventy diopters
Solution:

Chapter 27 Optical Instruments Q.109PP
Suppose a flexible, adaptive IOL has a focal length of 3.00 cm.How far forward must the IOL move to change the focus ofthe center from an object at infinity to an object at a distance of50.0 cm?
A. 1.9 mm
B. two.eight mm
C. 3.one mm
D. 3.ii mm
Solution:

Affiliate 27 Optical Instruments Q.110IP
IP Referring to Example 27–2 Suppose a person'southward eyeglasses have a focaL length of −301 cm, are 2.00 cm in front of the eyes, and allow the person to focus on distant objects. (a) Is this person's far indicate greater than or less than 323 cm, which is the far point for glasses the same altitude from the eyes and with a focal length of −321 cm? Explicate. (b) Find the far signal for this person.
Solution:

Chapter 27 Optical Instruments Q.111IP
IP Referring to Case 27–2 hi Instance 27–2, a person has a far-point distance of 323 cm. If this person wears spectacles 2.00 cm in front of the eyes with a focal length of −321 cm, afar objects tin can be brought into focus. Suppose a 2nd person'southward far signal is 353 cm. (a) Is the magnitude of the focal length of the eyeglasses that allow this person to focus on afar objects greater than or less than 321 cm? Presume the glasses are ii.00 cm in front of the eyes. (b) Discover the required focal length for the second person's eyeglasses.
Solution:

Chapter 27 Optical Instruments Q.112IP
IP Referring to Example 27–3 Suppose a person's eyeglasses have a refractive power of 2.75 diopters and that they allow the person to focus on an object that is only 25.0 cm from the eye. The spectacles are ii.00 cm in front of the optics. (a) Is this person's near point greater than or less than 57.0 cm, which is the near-point distance when the glasses have a refractive power of 2.53 diopters? Explicate. (b) Find the nearly indicate for this person.
Solution:

Affiliate 27 Optical Instruments Q.113IP
IP Referring to Example 27–3 Suppose a person's near-point distance is 67.0 cm. (a) Is the refractive power of the eyeglasses that permit this person to focus on an object just 25.0 cm from the eye greater than or less than 2.53 diopters, which is the refractive ability when the near-point distance is 57.0 cm? The glasses are worn 2.00 cm in front of the eyes. (b) Discover the required refractive power for this person's eyeglasses.
Solution:

Source: https://www.aplustopper.com/mastering-physics-solutions-chapter-27-optical-instruments/
0 Response to "Your Favorite Aunt Can Read a Newspaper Only if It Is Within 11.0 Cm of Her Eyes."
Post a Comment